NASA unveiled the initial images obtained from its Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of Pollution (TEMPO) mission. This space-based tool, created to assess air quality over North America, was launched earlier this year and supplies detailed data on major air contaminants to back clean air efforts and the Biden Administration’s climate objectives. These groundbreaking images have displayed unprecedented levels of detail in tracking air pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and ozone, enabling scientists to gain new insights into their impacts and distribution across the continent. Furthermore, TEMPO’s data will not only contribute to improving existing air quality models but also support policy-making and targeted measures to mitigate air pollution, safeguarding public health and fostering a sustainable environment.
TEMPO’s Monitoring Capabilities
Located 22,000 miles over the equator, TEMPO is expected to provide critical data regarding pollution resulting from peak traffic hours, fumes and debris produced by forest fires and volcanic eruptions, and the consequences of applying fertilizers on agricultural lands. By closely monitoring these pollution sources, the satellite aims to improve air quality forecasting and assist decision-makers in implementing effective pollution control measures. Furthermore, the data collected by TEMPO will enhance our understanding of the complex relationship between pollution and climate change, ultimately contributing to more sustainable practices worldwide.
Advancing Knowledge of Air Quality Inequalities
The gathered information will enable researchers to investigate the health effects of pollutants and develop air pollution maps on a neighborhood scale, thus advancing knowledge of air quality inequalities. Associated organizations such as the Environmental Protection Agency and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration will also have access to this information. By utilizing this data, these organizations can devise targeted interventions and policies to address specific areas with poor air quality, ultimately leading to healthier communities. Furthermore, schools, hospitals, and businesses can also benefit from localized air pollution monitoring, enabling them to make informed decisions on their practices and ensure the well-being of individuals.
TEMPO’s Launch and Current Monitoring Activities
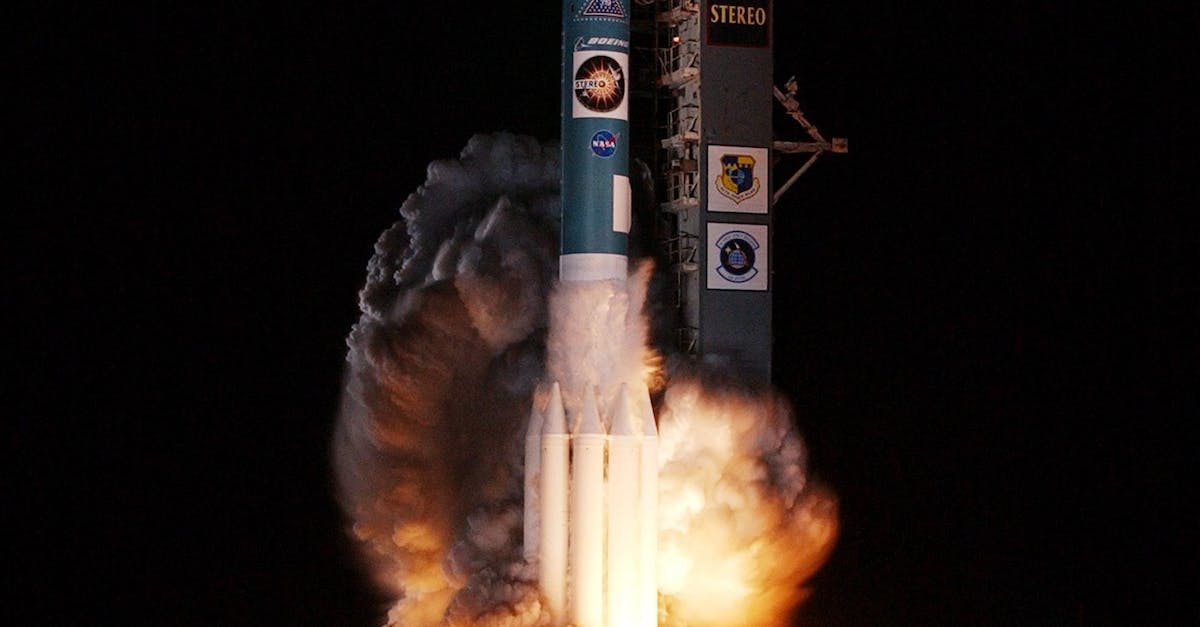
TEMPO was launched on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, along with a Maxar Intelsat 40e satellite, in April and performs hourly daytime monitoring of lower atmospheric conditions throughout North America. This cutting-edge technology provides vital data to scientists and researchers, paving the way for more accurate weather predictions and better understanding of climate change effects. With the ability to measure air pollutants, TEMPO also assists in monitoring and managing air quality, benefiting both the environment and public health.
Innovative Spectrometer and Collaboration
It is equipped with an advanced spectrometer that detects pollution in reflected sunlight. The mission represents a partnership between NASA and the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) located in Cambridge, Massachusetts. This collaboration aims to enhance the understanding of significant environmental changes and their impacts on our planet. By collecting precise data on air quality and pollution levels, the spectrometer allows scientists to monitor and address these concerns more effectively.
Progress Towards Full-Scale Operations
Since the launch, teams from NASA, Ball Aerospace, and SAO have been examining and fine-tuning TEMPO’s systems and parts. Recently, they have made significant progress in optimizing the instrument’s performance and ensuring its readiness for deployment. As a result, TEMPO is now much closer to its ultimate goal of providing accurate and timely air quality measurements from space, enabling researchers and policymakers to make well-informed decisions to protect our planet.
Looking Ahead: The Future of TEMPO’s Impact
Full-scale operations are set to commence in October, making TEMPO the pioneering instrument to monitor pollution over North America in this unique way. This innovative approach will enable researchers and policymakers to better understand the sources, distribution, and impacts of air pollution on a granular level. Consequently, it will aid in developing more effective strategies for mitigating pollution and improving overall air quality across the continent.
FAQs
What is NASA’s TEMPO mission?
TEMPO, short for Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of Pollution, is a space-based mission designed to monitor and assess air quality over North America. The satellite provides detailed data on major air pollutants, such as nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and ozone, to support clean air efforts and inform climate policies.
How does TEMPO monitor air pollution?
TEMPO is equipped with an advanced spectrometer that detects pollution in reflected sunlight. Located 22,000 miles over the equator, the satellite gathers critical data on various pollution sources, including traffic, forest fires, volcanic eruptions, and agricultural activities. The information collected aids in understanding the complex relationship between pollution and climate change, and supports the development of effective pollution control policies.
What are the benefits of TEMPO’s air quality data?
The data collected by TEMPO helps improve air quality forecasting, enhance existing air quality models, and strengthen the understanding of air quality inequalities. This information can be used by organizations like the Environmental Protection Agency and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration to create targeted interventions and policies. Localized monitoring also benefits schools, hospitals, and businesses by helping them make informed decisions on their practices to ensure public health and well-being.
When was TEMPO launched?
TEMPO was launched in April on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, along with a Maxar Intelsat 40e satellite. Since its launch, it has been performing hourly daytime monitoring of lower atmospheric conditions across North America.
Which organizations are involved in the TEMPO mission?
The mission represents a partnership between NASA and the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) located in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Teams from NASA, Ball Aerospace, and SAO have been working together to examine and fine-tune TEMPO’s systems and components.
When will TEMPO’s full-scale operations begin?
Full-scale operations for TEMPO are set to commence in October. This will make it the pioneering instrument to monitor pollution over North America in this unique way, providing valuable data for researchers and policymakers to develop more effective strategies for mitigating pollution and improving air quality.
First Reported on: spaceref.com
Featured Image Credit: Photo by Pixabay; Pexels; Thank you!